1、 Evaporation plating
1. definition
Evaporation is the process of evaporating a material to a solid surface by heating it.
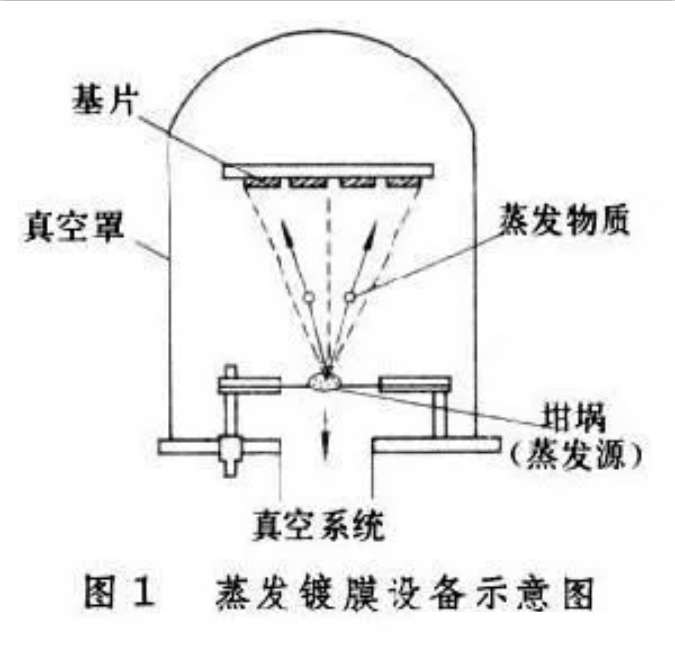
The structure of evaporation coating equipment is shown in Figure 1.
2. principle
Evaporated materials such as metals and compounds are placed in the crucible or hung on the hot wire as the source of evaporation, and the workpiece to be plated, such as metal, ceramics, plastics and other substrates are placed in front of the crucible. After the system is pumped to a high vacuum, the crucible is heated to evaporate the substance in it. The atoms or molecules of evaporated matter are deposited on the substrate surface by condensation.
The film thickness can be from hundreds of Angstroms to several microns. The thickness of the film depends on the evaporation rate and time of the evaporation source (or the charge), and is related to the distance between the source and the substrate. For large area coating, rotating substrate or multiple evaporation sources are often used to ensure the uniformity of film thickness. The distance from the vapor source to the substrate should be less than the average free path of the vapor molecule in the residual gas, so as to avoid the chemical effect caused by the collision between the vapor molecule and the residual gas molecule. The average kinetic energy of vapor molecules is about 0.1-0.2 ev.
3. types
There are three types of steam sources:
① Resistance plus heat source: made of refractory metals such as tungsten and tantalum into boat foil or silk shape, and heated by electric current above or in the crucible. Resistance heating source is mainly used for evaporation of CD, Pb, Ag, Al, Cu, Cr, Au, Ni and other materials.
② High frequency induction heating source: use high frequency induction current to heat crucible and evaporated substance.
③ Electron beam plus heat source: bombard the material with electron beam to make it evaporate. It is suitable for materials with high evaporation temperature (not lower than 2000 ℃).
4. characteristics
It can deposit films of metals, semiconductors, insulators, alloys, compounds with different composition ratios and some basic polymers on the surfaces of metals, semiconductors, insulators and even plastics, paper and fabrics. Its application range is incomparable with other methods. The films can be deposited at different deposition rate, substrate temperature and incidence angle of vapor molecules, so the films with different microstructure and crystal morphology (single crystal, polycrystalline or amorphous, etc.) can be obtained. The purity of the films is very high. It is easy to detect and control the thickness and composition of the films online. The thickness control accuracy can reach the order of single molecular layer.
Two sputtered plating
1. definition
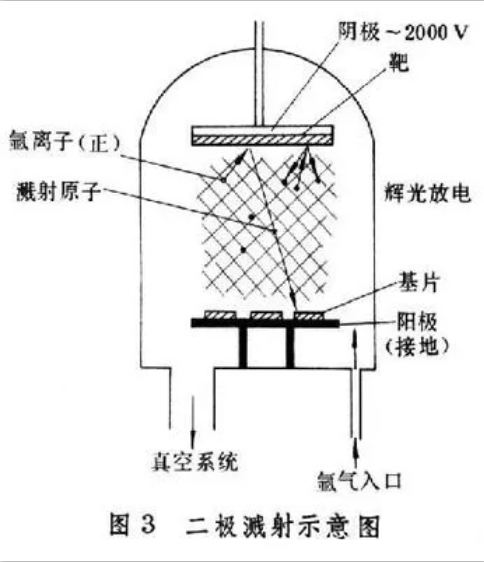
When the high energy particles bombard the solid surface, the particles on the solid surface can obtain energy and escape from the surface and deposit on the substrate. The commonly used two pole sputtering equipment is shown in figure [diagram of two pole sputtering].
2. principle

Usually, the material to be deposited is made into a plate target, which is fixed on the cathode. The substrate is placed on the anode facing the target and a few centimeters away from the target. The system is pumped to high vacuum and then filled with 10~1 PA gas (usually argon). The positive ions produced by the discharge fly to the cathode under the action of electric field and collide with the atoms on the target surface. The target atoms escaping from the target surface by collision are called sputtering atoms, and their energy ranges from 1 to dozens of electron volts. Sputtered atoms are deposited on the substrate.
3. classification
① Reactive sputtering method: the reactive gas (O, N, HS, CH, etc.) is added into Ar gas, and the reactive gas and its ions react with the target atom or sputtering atom to generate compounds (such as oxides, nitrides, etc.) and deposit on the substrate, which is suitable for sputtering compound film.
② High frequency sputtering. The base plate is installed on the grounded electrode and the insulation target is installed on the opposite electrode. One end of the high frequency power supply is grounded, and the other end is connected to the electrode equipped with the insulating target through the matching network and the DC isolating capacitor. After connecting the high frequency power supply, the high frequency voltage changes the polarity continuously. The electrons and positive ions in the plasma are deposited on the insulating target at the positive and negative half cycles of the voltage respectively. Because the electron mobility is higher than that of the positive ions, the surface of the insulating target is negatively charged. When the dynamic equilibrium is reached, the target is at a negative bias potential, which makes the sputtering of the positive ions on the target continue. It is suitable for sputtering insulating films.
4. characteristics:
The sputtering coating is not limited by the melting point of the film, but can be used to sputter W, Ta, C, Mo, WC, tic and other refractory materials. Splash plating has the advantages of strong adhesion between electroplated layer and substrate, compact and uniform electroplated layer, etc. The sputtered particles are not affected by gravity. The target and substrate can be arranged freely. The initial nucleation density of the film is high. It can produce extremely thin continuous films below 10nm. The target has a long life and can be produced automatically for a long time. The target material can be made into various shapes. With the special design of the machine for better control and more efficient production, the high-voltage electric field is used as the plasma coating material. Almost all high melting point metals, alloys and metal oxides, such as chromium, molybdenum, tungsten, titanium, silver and gold, are used. However, the processing cost is relatively high
1. definition
After the molecules of evaporated matter are ionized by electron collision, they are deposited on the solid surface with ions, which is called ion plating.
Ion plating is a combination of vacuum evaporation and cathode sputtering.
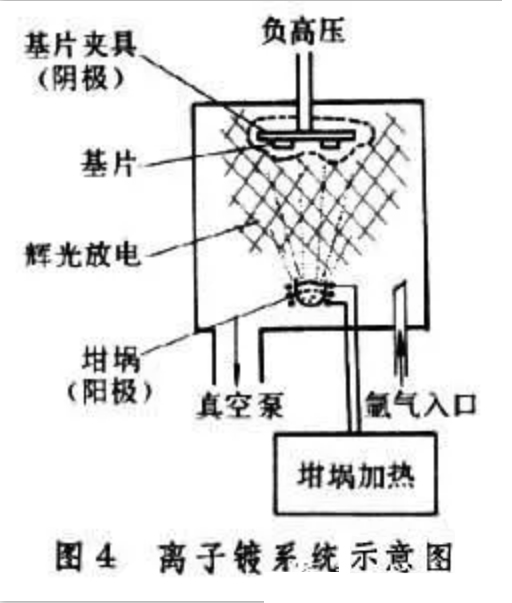
An ion plating system is shown in Figure 4 [schematic diagram of ion plating system]
2. principle
The evaporation source is connected with the anode, and the workpiece is connected with the cathode. When three to 5000 V high-voltage DC is applied, a glow discharge is generated between the evaporation source and the workpiece. Because the vacuum hood is filled with inert argon, part of the argon is ionized under the action of discharge electric field, thus forming a plasma dark area around the cathode workpiece. The positive charged argon ions are attracted by the negative high pressure of the cathode, which bombard the surface of the workpiece violently, causing the particles and dirt on the surface of the workpiece to be splashed out, so that the surface of the workpiece to be plated can be fully cleaned by ion bombardment. Then, turn on the AC power source of the evaporation source, the particles of the evaporation material melt and evaporate, enter the glow discharge area and are ionized. Under the attraction of the cathode, the positively charged evaporated material ions rush to the workpiece together with the argon ions. When the amount of evaporated material ions thrown on the workpiece surface exceeds the number of splashed ions, a layer of coating firmly adhered to the workpiece surface will gradually accumulate.
3. classification
① Magnetron sputtering ion plating
② Reactive ion plating
③ Hollow cathode discharge ion plating
④ Multi arc ion plating.
4. characteristics
The coating adhesion is good. The tensile test on the sample after ion plating shows that the coating still extends with the base metal in a plastic way until it is about to break, without peeling or peeling; the plating ability is strong, so this method is very suitable for the inner holes, grooves, narrow seams and other parts that are difficult to be plated by other methods; the coating group with good coating quality and ion plating Compact weaving, no pinhole, no bubble, uniform thickness; simple cleaning process.

